Several years ago, people at Ebony Horse Club in the UK, sought help after noticing how frustrated their Shetland pony Pedro was when he tried to see eye-to-eye with visitors. Standing at just 8 hands tall, Pedro struggled to see out over his stall door when he first arrived at the horse club.
1. What is Pedro’s height in centimetres?
2. What is Pedro’s height in inches?

Here’s one person’s idea for helping Pedro—high heels!
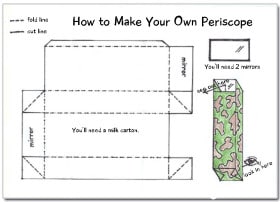
Given the challenge of creating something to help Pedro see over his door, kids at the club came up with different ideas. One girl thought of attaching large helium balloons to give the pony a lift, another designed four individual high heel shoes that could be fitted to Pedro’s hooves. Once all the ideas were collected, a vote was held. And the winning idea was—a periscope!
Science Talk – periscope: A periscope works on the Laws of Reflection. The light from the object falls on one mirror (placed at 45° to the object) and is reflected. This reflected light in turn falls on another mirror and is again reflected until it reaches the eye, in this case, Pedro’s.
Andy Morris, owner of Print and Cut, said: “We got an email from the Ebony Horse Club who were asking for our help, it was so nice, and a little bit funny, that we decided to give it a go.”
Andy said: “The sketch was sent to us and then I turned it into a 3D sketch with some software, and then it was sent to be made. It was all quite easy, and we did it for free to help Pedro.
3. What does 3D mean?
Gavin Hall, built the periscope, and being used to creating features for shop windows and banners, he was a little surprised when the job of building a periscope for a pony came through.
Gavin said: “It took me about three hours so it wasn’t too bad really, but it was a strange few hours working on a pony periscope.”
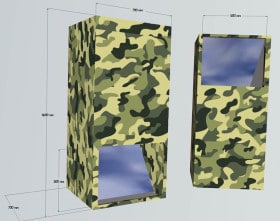
4. What is the height of Pedro’s periscope in cm?
5. What is the width of Pedro’s periscope in cm?
6. What are the dimensions of the mirror openings in metres?
7. What kind of quadrilateral is the opening?
When you are making a periscope, it’s important to make sure that the mirrors are positioned at 45-degree angles.
8. What kind of angle is 45 degrees?
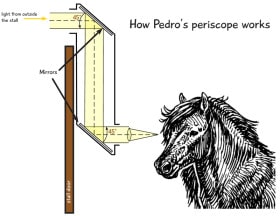
How does Pedro’s periscope work?
Light always reflects away from a mirror at the same angle that it hits the mirror (this is part of the Law of Reflection). In Pedro’s periscope, light from outside his stall hits the top mirror at a 45-degree angle and reflects away at the same angle, down through the periscope to the bottom mirror. That reflected light hits the second mirror at a 45-degree angle and reflects away at the same angle, right into Pedro’s eye!
Here’s a great video telling the whole story. You’ll see Pedro, the people at his stable, the kids developing their designs, and then, of course, the Pedroscope!
Answers:
1. What is Pedro’s height in centimetres?
Answer: 1 hand = 10.2 cm
8 × 10.2 = 81.6. Pedro is 82 cm high.
2. What is Pedro’s height in inches?
Answer: 1 hand = 4 inches
8 hands (Pedro’s height) × 4 (number of inches in one hand) = 32 inches. Pedro is 32 inches high. Pedro’s stall door was 1.5m high!
3. What does 3D mean?
Answer: 3D refers to three dimensions, height, width and depth.
4. What is the height of Pedro’s periscope in cm?
Answer: 1600 mm = 160 cm. Pedro’s periscope is 160 cm high.
5. What is the width of Pedro’s periscope in cm?
Answer: 700 mm = 70 cm. Pedro’s periscope is 70 cm wide.
6. What are the dimensions of the mirror openings in metres?
Answer: 500mm = .5m. The mirror openings are .5m high and wide.
7. What kind of quadrilateral is the opening?
Answer: Square. All four sides are the same length, and each interior angle is 90°.
8. What kind of angle is 45 degrees?
Answer: Acute. It is < 90°.
Common Core:
4.MD.A.1 – Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units
4.MD.C.5 – Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and understand concepts of angle measurement:
4.G.A.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures.
4.G.A.2 Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, or the presence or absence of angles of a specified size.
5.MD.A.1 – Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system
5.G.B.4 Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
Photos:
Pony in stall; CC0 Public Domain
High heels; YouTube screen shot
Periscope plans courtesy of Andy Morris, owner of Print and Cut